Minecraft Display Entities: A Comprehensive Guide for Customization and Creativity
Published:
Display entities are a powerful feature introduced in Minecraft 1.19.4 that allow map and data pack creators to showcase various elements within the game. With the ability to display blocks, items, and texts, display entities open up new possibilities for creativity and customization. In this tutorial, we’ll explore what display entities are, their usefulness in creating custom models in vanilla Minecraft, and why they are a better solution than using mods or custom resource packs.
Leveraging the Power of Vanilla Minecraft
While mods and custom resource packs have their place in enhancing Minecraft’s visuals, display entities prove that vanilla Minecraft features can deliver great solutions for customization. With display entities, you can create stunning custom models without relying on external modifications, tapping into the built-in capabilities of the game itself.
Understanding Display Entities
Display entities are a special type of entity that allows for the presentation of blocks, items, and text within the Minecraft world, all without the need for complex mods or plugins. There are three types of display entities: Block Display, Item Display, and Text Display, each serving a specific purpose. You can summon display entities using the /summon or /execute summon commands, providing flexibility in their placement and usage.
Comparing Display Entities to Other Solutions
Let’s take a closer look at how display entities compare to other existing solutions in Minecraft:
Block Displays vs. Armor Stands: Although armor stands have been commonly used for displaying blocks, block displays offer superior flexibility and control. With block displays, you can precisely position and showcase blocks, enabling intricate designs and complex arrangements.
Item Displays vs. Item Frames: While item frames have long been popular for displaying items, item displays take it a step further. In addition to showcasing items in any size and orientation, item displays support custom models using the
custom_model_datafeature, unlocking endless possibilities for unique item displays.Text Displays vs. Sign Blocks and Custom Name Tags: Traditional methods of displaying text involved sign blocks and custom name tags. However, text displays offer more versatility and control over the appearance of text. You can specify alignment, background color, line width, opacity, and more, allowing for visually stunning text displays that seamlessly integrate into your Minecraft world.
Example /summon Commands
To demonstrate the potential of block displays, here are a few example /summon commands showcasing their usage:
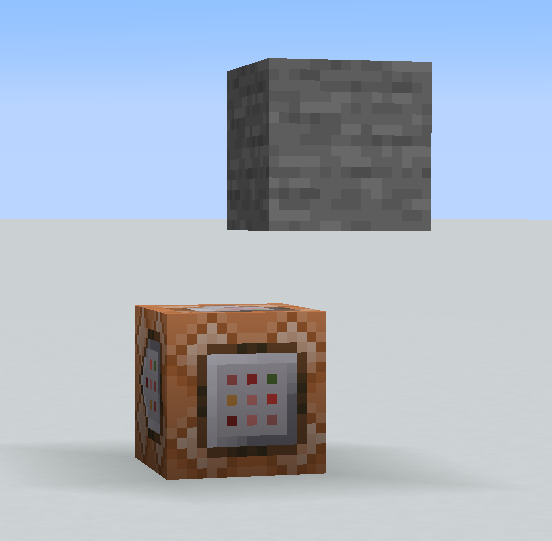
1. Summoning a Block Display:
/summon minecraft:block_display ~ ~1 ~ {block_state:{Name:"minecraft:stone"}}
This command summons a block display showcasing a stone block at the current location.

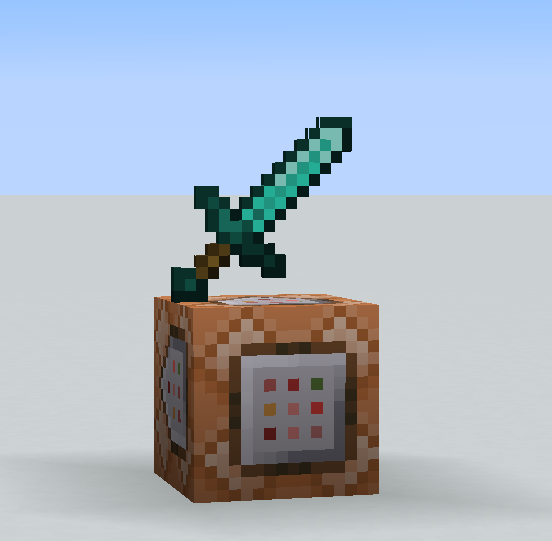
2. Summoning an Item Display:
/summon minecraft:item_display ~ ~1 ~ {item:{id:"minecraft:diamond_sword",Count:1}}
This command summons an item display with a diamond sword.

3. Summoning a Text Display:
/summon minecraft:text_display ~ ~1 ~ {text:"{\"text\":\"Welcome to BDStudio!\",\"color\":\"green\",\"bold\":true}"}
This command summons a text display with a bold, green-colored message saying “Welcome to BDStudio!”

Exploring NBT Tags for Display Entities
To further customize and refine your display entities, let’s delve into the NBT tags common to all display entities:
billboard: Controls whether the entity pivots to face the player when rendered. Options include fixed, vertical, horizontal, and center.brightness: Overrides the light values used for rendering, specifying block-light and skylight levels.glow_color_override: Overrides the glow border color. Use 0 to utilize the team color the display entity belongs to.height: Sets the maximum height of the entity, allowing for culling and precise positioning.width: Determines the maximum width of the entity, offering culling capabilities and precise alignment.interpolation_durationandstart_interpolation: Enable the interpolation of visual effects over time, creating smooth animations.shadow_radiusandshadow_strength: Control the presence and opacity of shadows cast by the entity.view_range: Defines the maximum view range of the entity, allowing for visibility adjustments based on distance.transformation: Applies rendering transformations to the model, including rotation, scaling, and translation.
By utilizing these NBT tags, you can achieve breathtaking visual effects and fine-tune the appearance of your display entities to match your creative vision.
For additional tags used by the different types of display entities please visit the Minecraft Wiki’s page.
The Power of Transformation
The transformation tag in display entities allows you to apply rendering transformations to the model, adjusting its orientation and position in relation to the entity’s origin. This tag is the key to achieving precise control over how the model is displayed within the game. The transformation tag can be specified in two forms: matrix form and decomposed form.
Matrix Form: In the matrix form, the
transformationtag is a list of 16 float numbers, representing a row-major matrix. Each element in the matrix corresponds to a value used in the transformation calculations.Decomposed Form: In the decomposed form, the
transformationtag is a compound tag with sub-tags that are applied sequentially. The decomposed form consists of the following sub-tags:right_rotation: Specifies the initial rotation using quaternion form or axis-angle form. If quaternion form is used, it is represented by a list of four float numbers. If axis-angle form is used, it is represented by a compound tag with two sub-tags:angle(the angle of rotation) andaxis(the axis vector with three elements).scale: Determines the scale of the model centered on the origin. This tag is a list of three float numbers representing the scaling factors along each axis.left_rotation: Represents an additional rotation applied to the model. Similar toright_rotation, it can be specified in quaternion form or axis-angle form.translation: Specifies the translation transformation, moving the model from its original position. This tag is a list of three float numbers representing the translation along each axis.
Manipulating these transformation tags gives you unparalleled flexibility to rotate, scale, and position the model exactly as desired.
Example Transformation Tags:
In matrix form:
{
transformation: [
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
]
}
In decomposed form:
{
transformation: {
right_rotation: [0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f],
scale: [1.5f, 1.5f, 1.5f],
left_rotation: {
angle: 45.0f,
axis: [0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f]
},
translation: [2.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f]
}
}
Block display example:
/summon minecraft:block_display ~ ~1 ~ {block_state:{Name:"minecraft:stone"},transformation:{right_rotation:[0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f],scale:[1.5f, 1.5f, 1.5f],left_rotation:{angle:45.0f,axis:[0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f]},translation: [2.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f]}}
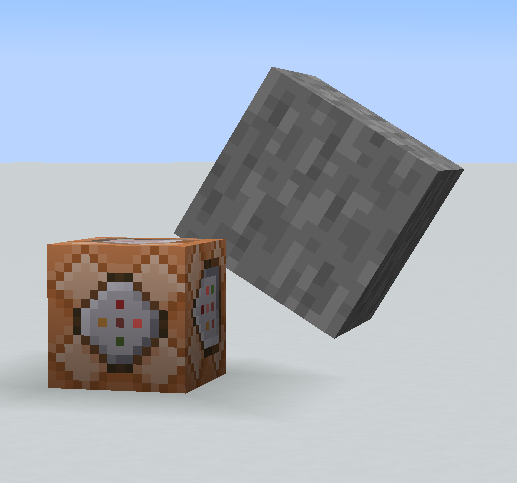
The transformation tag is considered the most powerful tag for display entities because it allows you to manipulate the orientation and position of the model in a highly customizable manner. Whether you want to rotate the model, scale it, or move it to a specific location, the transformation tag provides the tools to achieve your desired visual effects. Its matrix form offers precise control over the transformation using numerical values, while the decomposed form allows for easier manipulation through individual sub-tags. This level of flexibility empowers creators to bring their imaginative visions to life in Minecraft, elevating the possibilities for custom models and enhancing the overall gameplay experience.
Effortless Creation with BDStudio
BDStudio is a powerful tool that simplifies the process of creating transformations for block display entities in Minecraft. It offers an intuitive interface and user-friendly features, making it easy to design intricate block display models. BDStudio generates commands using the matrix form of the transformation tag, allowing users to adjust rotation, scale, and translation parameters interactively.
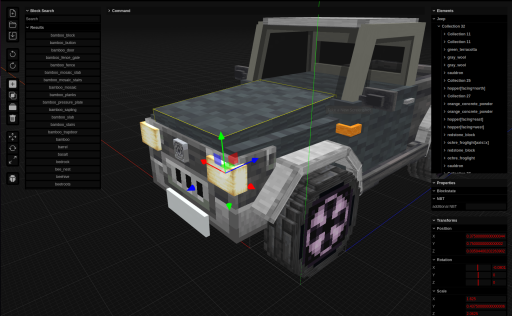
The tool provides real-time visual representation of the transformation and dynamically updates the matrix values as adjustments are made. Once the desired transformation is achieved, BDStudio generates the corresponding command, which can be seamlessly integrated into Minecraft without manual calculations or complex scripting.
BDStudio’s use of the matrix form enhances efficiency and convenience, eliminating the need for manual matrix calculations and reducing errors. It enables creators to implement even intricate transformations effortlessly, unlocking the full potential of the transformation tag and bringing imaginative visions to life.
I hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into display entities and their significance in creating custom models within vanilla Minecraft. Now it’s your turn to unlock your creativity, experiment with block displays, and bring your Minecraft projects to a whole new level of visual splendor.
Happy crafting!
